INTRODUCTION
In recent decades, the rapid development of industrialization and urbanization has resulted in enormous energy consumption. Faced with the energy crisis, people are paying more attention to energy conservation and emission reduction. Therefore, in 2015, the Paris Agreement proposed to control the increase in global average temperature within 2 ℃. Similarly, in 2020, China proposed the goals of achieving “carbon peak” and “carbon neutrality” by 2030 and 2060 respectively to reduce carbon emissions. Their purpose is to achieve environmental protection and sustainable development. Currently, building energy consumption accounts for approximately 30% of the total worldwide energy consumption. Due to the increasing demand for thermal comfort, the energy consumption of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems accounts for about half of building energy consumption. Therefore, improving the energy efficiency of HVAC systems is very important for achieving the goals of carbon neutrality.
In traditional HVAC systems, the cooling and heating of buildings are provided by chillers and boilers, respectively. On one hand, the combustion process of coal- and gas-fired boilers directly emits greenhouse gases, and the primary energy efficiency of electric boilers is low. On the other hand, the cooling and heating processes require two independent sets of equipment, which is more complex. Heat pumps have both cooling and heating functions, and their primary energy efficiency for heating is higher than that of boilers. Therefore, it has achieved rapid development in recent years.
According to the different heat sources, heat pumps can be divided into air source heat pumps (ASHPs), ground source heat pumps, waste heat source heat pumps, etc. Because air is not easily affected by space and time, the installation and use of ASHP units are relatively simple and convenient, so the application of ASHPs is the most common. Therefore, this paper mainly introduces the recent development of ASHPs in China.
CURRENT STATUS OF ASHPS IN CHINA
In this section, the current market of ASHPs in China is first introduced. Then, the application scenarios of ASHPs are illustrated, including buildings, industry, agriculture, and other industries. (Note: The data is sourced from the China Heat Pump Industry Development Report 2023.)
CURRENT MARKET
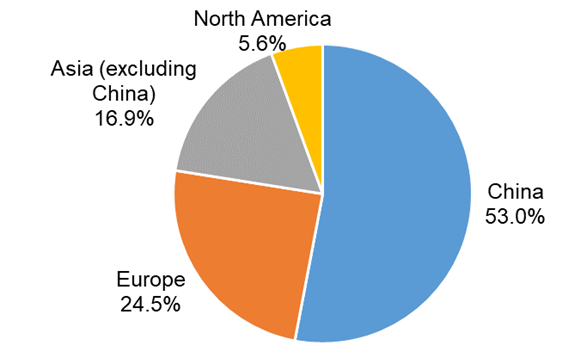
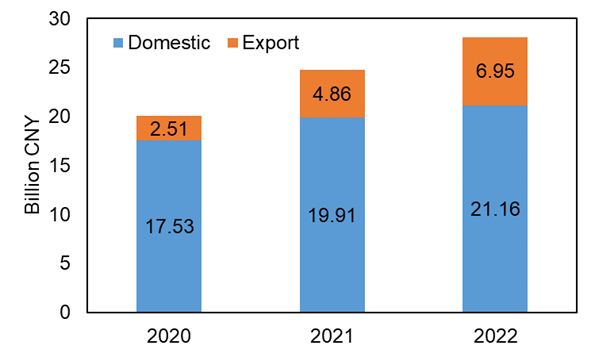
At present, China’s ASHP production is the highest globally, accounting for 53.0%, as shown in Fig. 1. In addition, Europe, other Asian countries, and North America are also the main providers of ASHPs. Specifically, Fig. 2 shows the ASHP market in China. The domestic sales of ASHPs are much higher than the export sales, and both are increasing year by year. However, the growth rate of export sales is significantly higher than that of domestic sales. Compared to 2021, the growth rates of domestic sales and export sales in 2022 were 6.3% and 43.0%, respectively. Therefore, the proportion of exports is rapidly increasing, from 12.5% in 2020 to 24.7% in 2022.
According to different applications, the domestic market can be further divided into hot water, heating, and drying, as shown in Fig. 3. From Fig. 3 (a), heating remains the main application of ASHP, with sales reached 12.07 billion CNY in 2022. And the sales of heating and drying have been continuously increasing. Similarly, from Fig. 3 (b), the proportion of heating and drying is also increasing. However, due to the impact of the real estate market, the proportion of hot water is decreasing. It can be inferred that heating is the main driving force for the development of ASHP.
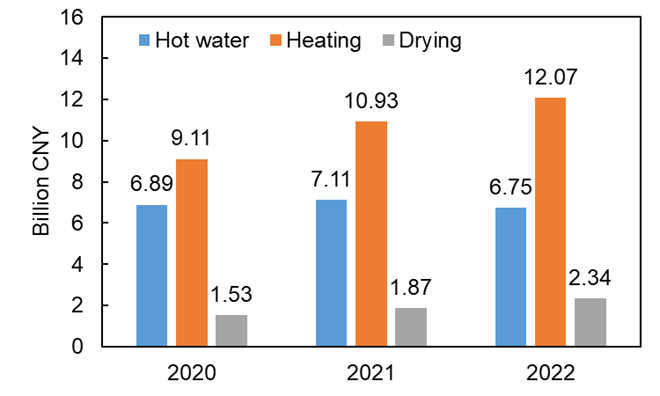
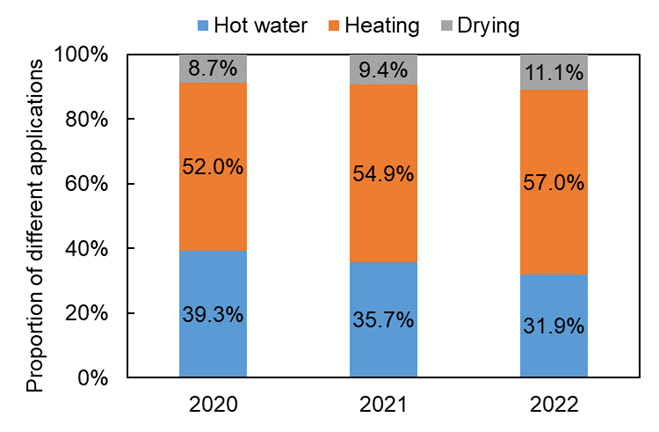
Fig. 3. ASHP’s domestic market in China.
The compressor is the most important component of a heat pump, Fig. 4 shows the current market for compressors of ASHP. Regarding different types in Fig. 4(a), the scale of rotary compressors has reached 3.2 million units in 2022, accounting for 82.0% of the market share and a year-on-year increase of 10.4%. Affected by the poor hot water market, the sales of scroll compressors have slightly declined, with a year-on-year decline of about 5% in 2022. The scale of screw compressors continues to expand, with a growth of 12.5% in 2022 compared to 2021.
Regarding different applications in Fig. 4(b), rotary compressors are mainly used for hot water and heating, and the combined proportion of the two accounts for almost all. The application proportion of scroll compressors in hot water is the highest, accounting for 54.2%. In addition, the proportion used for drying of scroll compressors has increased rapidly in recent years, reaching 12.1% in 2022. The screw compressor is generally only used for heating.
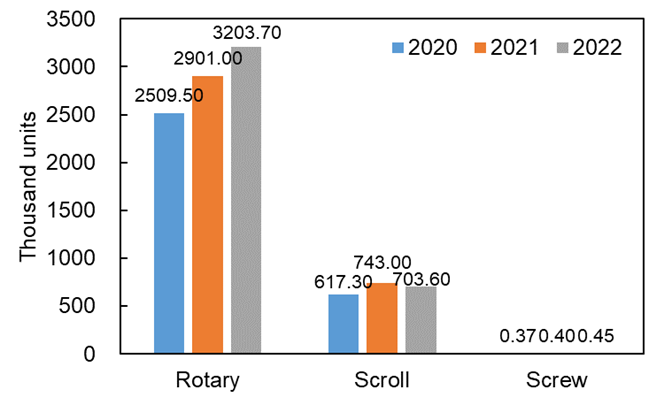
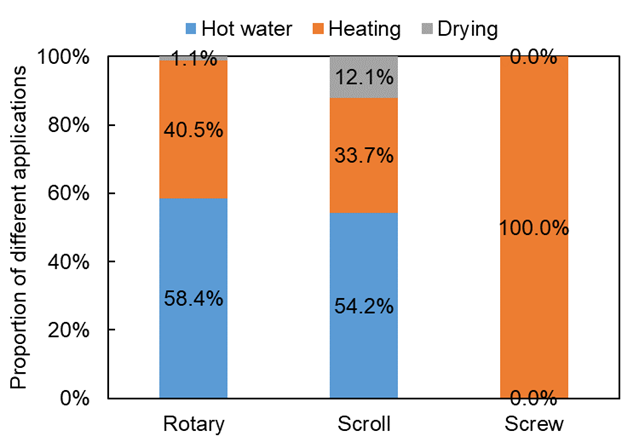
Fig. 4. Current market of compressors in China.
PROSPECT OF ASHP APPLICATION
In the future, ASHPs will be more widely used in building, industry, agriculture, etc., as follows.
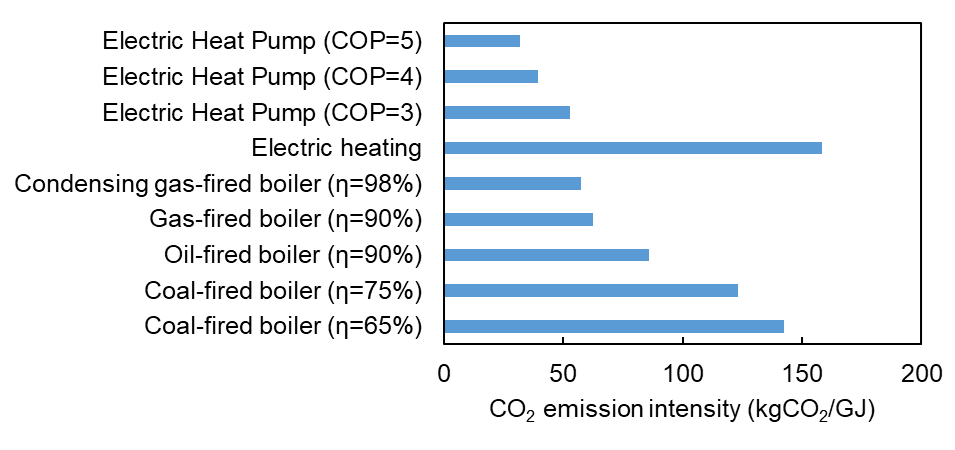
(1) Since 2014, the annual completed floor area of residential and commercial buildings in China has generally exceeded 4 billion square meters, leading to a continuous high-speed growth in building area. Therefore, the carbon emissions of building sector continue to increase. There are various ways for space heating, but the carbon dioxide emissions per 1GJ of heating are different, as shown in Fig. 5. It can be seen that heat pumps are the most effective way to reduce emissions, and they can be applied to new buildings and existing building renovations.
(2) The industrial sector has a heat demand of 2.11 billion GJ below 80 ℃, and a heat demand of 2.10 billion GJ between 80 ℃ and 160 ℃, as listed in Table 1. Heat pumps can be widely used for heat demand below 160 ℃, such as high-temperature industrial heat pumps, waste heat recovery, industrial drying, and combined cooling and heating systems.
| Sort | < 80 ℃ (×109 GJ) | 80~160 ℃ (×109 GJ) | >160 ℃ (×109 GJ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural and sideline food processing | 1.812 | 1.087 | 0.725 |
| Food manufacturing | 0.299 | 2.092 | 0.598 |
| Wine, beverages, and refined teas | 0.789 | 1.577 | 0.263 |
| Spin | 0.433 | 1.516 | 0.217 |
| Wood processing | 0.152 | 0.607 | 0.758 |
| Papermaking | 0.563 | 1.689 | 3.378 |
| Oil and coal | 12.074 | 2.415 | 33.808 |
| Chemical engineering | 0.624 | 2.495 | 28.067 |
| Pharmaceutical manufacturing | 0.191 | 0.574 | 1.148 |
| Chemical fiber manufacturing | 0.212 | 0.424 | 1.485 |
| Rubber and plastic manufacturing | 0.428 | 0.855 | 2.992 |
| Non-metallic mineral products | 0.293 | 2.635 | 26.351 |
| Non-ferrous metal smelting | 0.215 | 1.931 | 19.312 |
| Metalwork | 1.534 | 0.288 | 0.096 |
| General equipment manufacturing | 0.743 | 0.212 | 0.106 |
| Special equipment manufacturing | 0.386 | 0.110 | 0.055 |
| Automobile manufacturing | 0.322 | 0.536 | 0.214 |
| Total | 21.068 | 21.043 | 119.572 |
(3) In terms of temperature regulation in agricultural facilities, it is mainly used for agricultural greenhouses and livestock and poultry houses. There are currently examples proving that heating by heat pumps in agricultural greenhouses can save 20-60% of energy consumption compared to coal-fired heating. In addition, heat pumps can also be used for drying agricultural and sideline products, such as wood, food, grains, seeds, fruits, vegetables, tobacco, etc.
(4) The transportation sector accounts for 23% of global greenhouse gas emissions and is the third largest source of greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, electric vehicles are the direction of future development, and automotive air conditioning with heat pump is the most promising solution to improve the range of electric vehicles.
TECHNOLOGIES FOR FUTURE DEVELOPMENT
Although heat pump technology has been studied for a long time, there are still some technologies that need to be developed in the future, mainly in compressors, emerging scenarios, and low GWP refrigerants.
Compressor
The compressor is the most important component of a heat pump, and the key technologies that need to be developed are as follows.
(1) Development of new compression technologies to improve compressor performance. For example, developing oil-free compressors, applying permanent magnet motors and inverter technology.
(2) Development of compressors with changeable compression ratio. The compression ratio is changed time by time. Current compressors are with less change of compression ratio. It is necessary to develop compressors that can change the compression ratio in a wide range.
(3) Development of components to be more matched with compressors to achieve energy efficiency improvement of the entire heat pump unit. The capacity of heat exchangers and other components is usually determined by the design conditions, which may be not energy-efficient in the off-design conditions.
Emerging scenarios
Heat pumps have various application scenarios, with different temperature requirements and operating characteristics in building, industry, agriculture, and transportation. Therefore, it is necessary to develop heat pumps suitable for different scenarios, especially those emerging scenarios.
(1) Low ambient temperature heat pump. The energy efficiency of ASHPs rapidly decreases under low-temperature conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to further develop low ambient temperature heat pumps to meet the application needs in cold regions.
(2) High temperature heat pump. The heat demand of many industries is higher than 100 ℃. Therefore, it is necessary to further develop high-temperature heat pump technology for producing steam and high-temperature hot water to meet more industrial applications.
(3) Electric vehicle heat pump. In recent years, electric vehicles have developed rapidly. As an important technology in the thermal management of electric vehicles, heat pumps will have a greater demand for electric vehicles in the future. Therefore, it is necessary to further develop energy-efficient heat pumps suitable for electric vehicles.
Low GWP Refrigerant
Refrigerant is a key concern for non-carbon dioxide emissions. The greenhouse effect of refrigerants is generally determined using global warming potential (GWP). In addition, refrigerants may also cause damage to the ozone layer, which is determined by the ozone depletion potential (ODP). In the future, there are mainly the following development directions for refrigerants.
(1) Alternative refrigerants. On one hand, natural refrigerants such as carbon dioxide, water, hydrocarbons, etc. can be used. On the other hand, it is necessary to further develop refrigerants with zero ODP, low GWP, lower toxicity and flammability.
(2) Through the improvement of technology, policies, and regulations, the use and recovery of refrigerants should be standardized to reduce refrigerant leakage.
(3) Research and development of refrigerants for special application scenarios. It should not only meet the environmental performance, but also adapt to special application scenarios such as high and low temperatures.
SUMMARY
In the context of energy conservation and emission reduction, the value of energy conservation, environmental protection, and low-carbon of heat pumps is receiving increasing attention both internationally and domestically in China. There is great expectation for the carbon reduction contribution of heat pumps. It can be foreseen that heat pumps will further develop under the promotion of carbon peak and carbon neutrality.
To better develop heat pumps, efforts can be made in the following areas in the future.
(1) Encourage the application of heat pump technology in different industries.
(2) Establish sound standards and application specifications for heat pump products.
(3) Enhance social awareness of heat pump technology from multiple aspects.
(4) Introduce more incentive policies to promote the application of heat pumps.
(5) Promote the entry of heat pumps into the carbon trading market and develop research on carbon trading methodologies.

Xiating Li

Wentao Wang

Huaqian Jing
